- Published on
Lane Model in React
Lane Model in React
面试题:是否了解过 React 中的
lane模型?为什么要从之前的expirationTime模型转换为lane模型?
React and Scheduler priorities
前面的文章有介绍 Scheduler,React 团队是打算将 Scheduler 进行独立发布。
React rendering process
Understanding React Delayed Task Scheduling
React Scheduler Task Scheduling
在 React 内部,还会有一个粒度更细的优先级算法,这个就是 lane 模型。
接下来来看一下两套优先级模型的一个转换。
在 Scheduler 内部,拥有 5 种优先级:
export const NoPriority = 0
export const ImmediatePriority = 1
export const UserBlockingPriority = 2
export const NormalPriority = 3
export const LowPriority = 4
export const IdlePriority = 5
作为一个独立的包,需要考虑到通用性,Scheduler 和 React 的优先级并不共通,在 React 内部,有四种优先级,如下四种:
export const DiscreteEventPriority: EventPriority = SyncLane
export const ContinuousEventPriority: EventPriority = InputContinuousLane
export const DefaultEventPriority: EventPriority = DefaultLane
export const IdleEventPriority: EventPriority = IdleLane
由于 React 中不同的交互对应的事件回调中产生的 update 会有不同的优先级,因此优先级与事件有关,因此在 React 内部的优先级也被称之为 EventPriority,各种优先级的含义如下:
DiscreteEventPriority:对应离散事件优先级,例如click、input、focus、blur、touchstart等事件都是离散触发的ContinuousEventPriority:对应连续事件的优先级,例如drag、mousemove、scroll、touchmove等事件都是连续触发的DefaultEventPriority:对应默认的优先级,例如通过计时器周期性触发更新,这种情况下产生的update不属于交互产生update,所以优先级是默认的优先级IdleEventPriority:对应空闲情况的优先级
在上面的代码中,我们还可以观察出一件事情,不同级别的 EventPriority 对应的是不同的 lane
既然 React 与 Scheduler 优先级不互通,那么这里就会涉及到一个转换的问题,这里分为:
- React 优先级转为
Scheduler的优先级 Scheduler的优先级转为 React 的优先级
Transfer React priorities to Scheduler priorities
整体会经历两次转换:
- 首先是将
lanes转为EventPriority,涉及到的方法如下:
export function lanesToEventPriority(lanes: Lanes): EventPriority {
// getHighestPriorityLane 方法用于分离出优先级最高的 lane
const lane = getHighestPriorityLane(lanes)
if (!isHigherEventPriority(DiscreteEventPriority, lane)) {
return DiscreteEventPriority
}
if (!isHigherEventPriority(ContinuousEventPriority, lane)) {
return ContinuousEventPriority
}
if (includesNonIdleWork(lane)) {
return DefaultEventPriority
}
return IdleEventPriority
}
- 将
EventPriority转换为Scheduler的优先级,方法如下:
// ...
let schedulerPriorityLevel
switch (lanesToEventPriority(nextLanes)) {
case DiscreteEventPriority:
schedulerPriorityLevel = ImmediateSchedulerPriority
break
case ContinuousEventPriority:
schedulerPriorityLevel = UserBlockingSchedulerPriority
break
case DefaultEventPriority:
schedulerPriorityLevel = NormalSchedulerPriority
break
case IdleEventPriority:
schedulerPriorityLevel = IdleSchedulerPriority
break
default:
schedulerPriorityLevel = NormalSchedulerPriority
break
}
// ...
举一个例子,假设现在有一个点击事件,在 onClick 中对应有一个回调函数来触发更新,该更新属于 DiscreteEventPriority,经过上面的两套转换规则进行转换之后,最终得到的 Scheduler 对应的优先级就是 ImmediateSchedulerPriority
Transfer Scheduler priorities to React priorities
转换相关的代码如下:
const schedulerPriority = getCurrentSchedulerPriorityLevel()
switch (schedulerPriority) {
case ImmediateSchedulerPriority:
return DiscreteEventPriority
case UserBlockingSchedulerPriority:
return ContinuousEventPriority
case NormalSchedulerPriority:
case LowSchedulerPriority:
return DefaultEventPriority
case IdleSchedulerPriority:
return IdleEventPriority
default:
return DefaultEventPriority
}
这里会涉及到一个问题,在同一时间可能存在很多的更新,究竟先去更新哪一个?
- 从众多的有优先级的
update中选出一个优先级最高的 - 表达批的概念 (一批一批的更新而不是一个一个的更新,同一种类型可以一起更新)
React 在表达方式上面实际上经历了两次迭代:
- 基于
expirationTime的算法 - 基于
lane的算法
expirationTime Model
React 早期采用的就是 expirationTime 的算法,这一点和 Scheduler 里面的设计是一致的。
在 Scheduler 中,设计了 5 种优先级,不同的优先级会对应不同的 timeout,最终会对应不同的 expirationTime,然后 task 根据 expirationTime 来进行任务的排序。
早期的时候在 React 中延续了这种设计,update 的优先级与触发事件的当前时间以及优先级对应的延迟时间相关,这样的算法实际上是比较简单易懂的,每当进入 schedule 的时候,就会选出优先级最高的 update 进行一个调度。
但是这种算法在表示 “批” 的概念上不够灵活。
在基于 expirationTime 模型的算法中,有如下的表达:
const isUpdateIncludedInBatch = priorityOfUpdate >= priorityOfBatch
priorityOfUpdate 表示的是当前 update 的优先级,priorityOfBatch 代表的是批对应的优先级下限,也就是说,当前的 update 只要大于等于 priorityOfBatch,就会被划分为同一批:
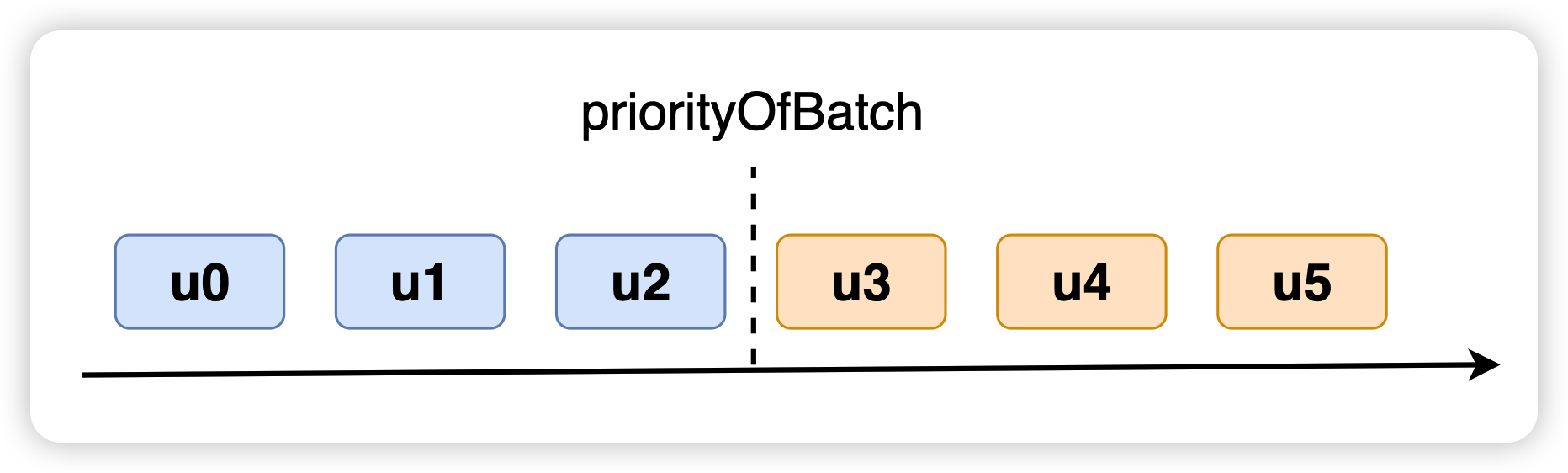
但是此时就会存在一个问题,如何将某一范围的某几个优先级划为同一批?
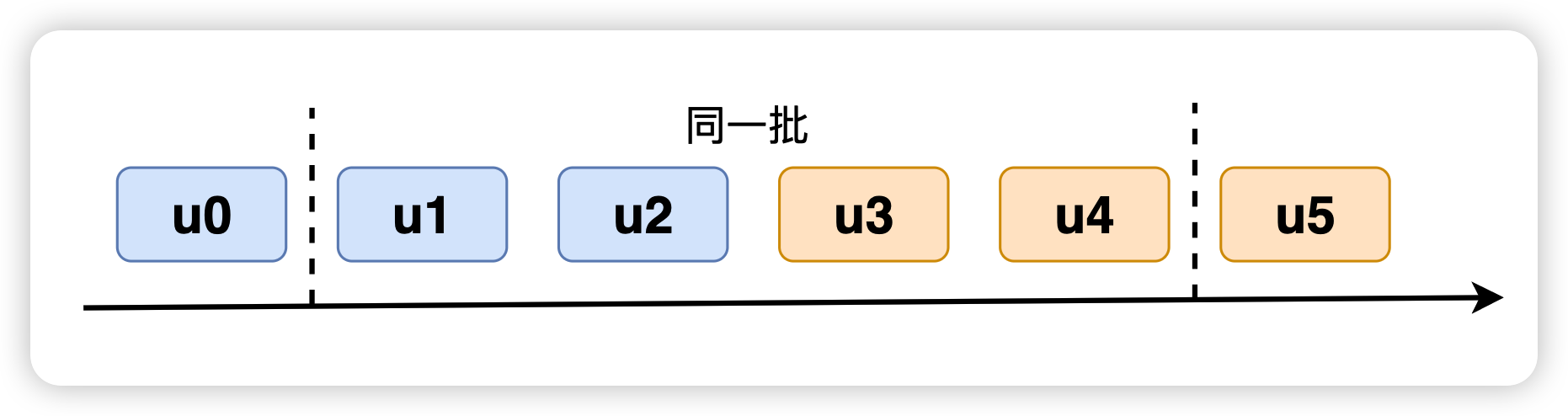
究其原因,是因为 expirationTime 模型优先级算法耦合了 “优先级” 和 “批” 的概念,限制了模型的表达能力。优先级算法的本质是为 update 进行一个排序,但是 expirationTime 模型在完成排序的同时还默认的划定了 “批”。
lane Model
因此,基于上述的原因,React 中引入了 lane 模型。
不管新引入什么模型,比如要保证以下两个问题得到解决:
- 以优先级为依据,对 update 进行一个排序
- 表达批的概念
针对第一个问题,lane 模型中设置了很多的 lane,每一个 lane 实际上是一个二进制数,通过二进制来表达优先级,越低的位代表越高的优先级,例如:
export const SyncLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000000001
export const InputContinuousLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000000100
export const DefaultLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0000000000000000000000000010000
export const IdleLane: Lane = /* */ 0b0100000000000000000000000000000
export const OffscreenLane: Lane = /* */ 0b1000000000000000000000000000000
在上面的代码中,SyncLane 是最高优先级,OffscreenLane 是最低优先级。
对于第二个问题,lane 模型能够非常灵活的表达批的概念:
// 要使用的批
let batch = 0
// laneA 和 laneB。是不相邻的优先级
const laneA = 0b0000000000000000000000001000000
const laneB = 0b0000000000000000000000000000001
// 将 laneA 纳入批中
batch |= laneA
// 将 laneB 纳入批中
batch |= laneB
真题解答
题目:是否了解过 React 中的 lane 模型?为什么要从之前的
expirationTime模型转换为 lane 模型?参考答案:
在 React 中有一套独立的粒度更细的优先级算法,这就是 lane 模型。
这是一个基于位运算的算法,每一个 lane 是一个 32 bit Integer,不同的优先级对应了不同的 lane,越低的位代表越高的优先级。
早期的 React 并没有使用 lane 模型,而是采用的的基于
expirationTime模型的算法,但是这种算法耦合了**“优先级”** 和 “批” 的概念,限制了模型的表达能力。优先级算法的本质是“为 update 排序”,但expirationTime模型在完成排序的同时还默认的划定了 “批”。使用 lane 模型就不存在这个问题,因为是基于位运算,所以在批的划分上会更加的灵活。